Bluetooth connection problems can appear to be a problem if you are running a Linux-based Kali Linux system. As glorious as Linux is for providing the ultimate road to technological freedom, there are still some ways that we have to travel before we can all be trucking around only in Linux vehicles. One such cunning feature is Bluetooth. This quick guide will show you how to turn on (or off) Bluetooth, check whether there’s Bluetooth support, and connect a Bluetooth device.
Whether a Linux beginner or an advanced user, you’ll learn a thing or two right here that will take the mystery out of getting Bluetooth to work again.
Why Does Bluetooth Work so Differently on Linux?
It is frequently said that Bluetooth is a major offender when it comes to operating systems, and for Linux it is often mentioned.
But before getting into the how, we need to understand the why. In contrast to a proprietary operating system, Linux needs modules and drivers developed by users to support various hardware. On Linux, Bluetooth functionality often relies on correct installation and configuration of such things as Bluez, kernel modules, and services being enabled. After you configure it, Linux Bluetooth is just as good as Bluetooth on other OSes.
Now lets cipher into the solution
Step 1: Ensure Your Bluetooth Hardware is Working
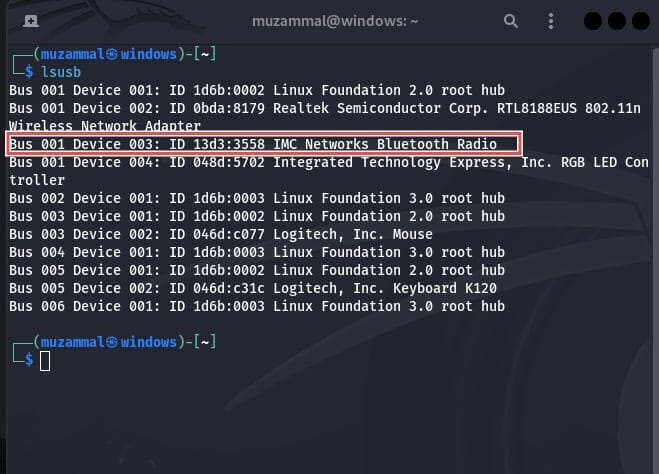
The first thing you need to do is to verify whether your system has Bluetooth hardware or not. Open terminal and run the following command.
lsusbGo to Connected USB Devices, if your Bluetooth Adapter is registered then you will see Bluetooth in it.
If not:
Ensure Your Computer Has Bluetooth Check your computer specifications to confirm it has built-in Bluetooth.
Where you are using VM, you need to attach USB Bluetooth to the host machine and enable USB passthrough in your VM settings.
(Tip: If your adapter is not listed, plug it into another USB port or reboot your VM to reinitialize USB connections.)
Now step 2 is Installing Bluez (The Bluetooth Toolkit)
sudo apt update && sudo apt install bluez
Get a coffee while it installs. When you are finished, press y for upgradeing. you’ve set up the following system for allowing Bluetooth to work <3
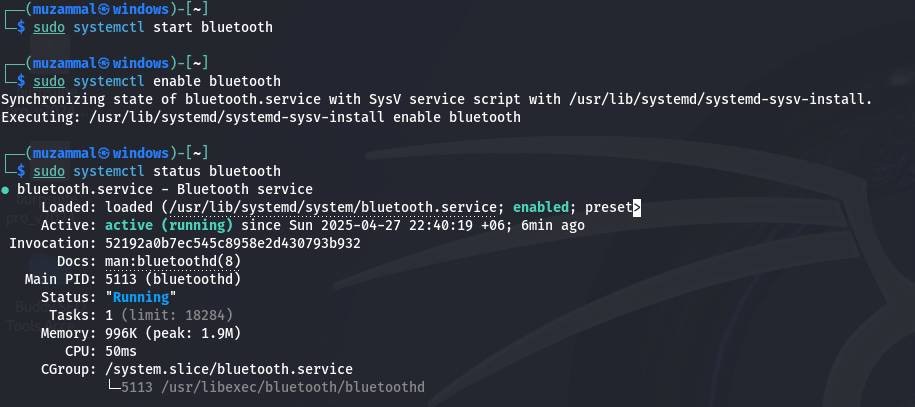
Step 3: Turn on the Bluetooth Service.
The Bluetooth toolkit is just the beginning. What we must do next is to start up the bluetooth service. Open your terminal and enter:
sudo systemctl start bluetoothsudo systemctl enable bluetoothTo verify whether the service is running run:
sudo systemctl status bluetoothYou should see “active (running)” in the output. If not, please double-check your Bluez installation, or reboot your system.
Step 4: Unblock Bluetooth
Linux occasionally “rejects” Bluetooth connections for security or power saving purposes. Run the following to see if Bluetooth is hardblocked:
rfkill listIf you see “Soft blocked” or “Hard blocked” next to Bluetooth, unblock it with:
rfkill unblock bluetooth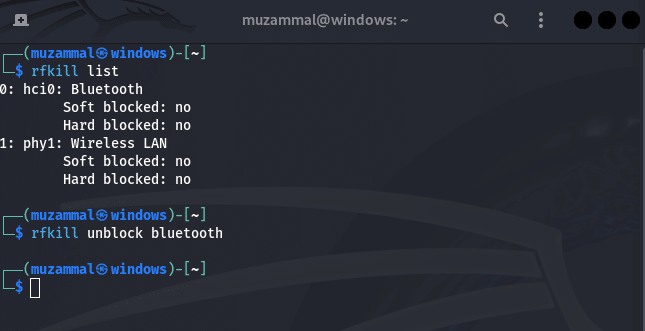
Think of this command as preventing a lock from blocking the access of Bluetooth operations.
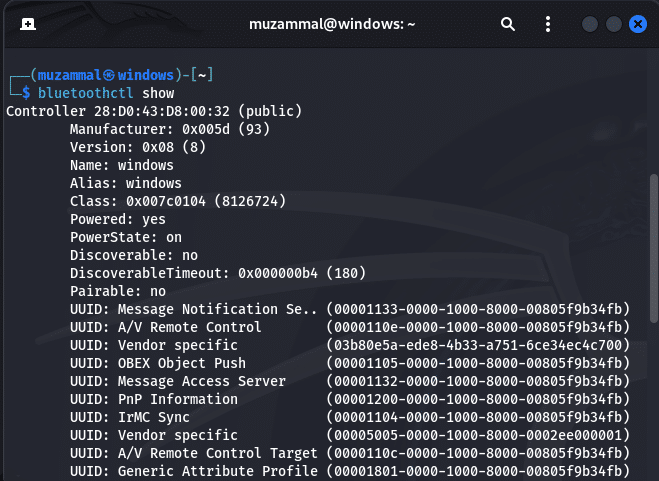
Step 5: Validate the Status of Bluetooth
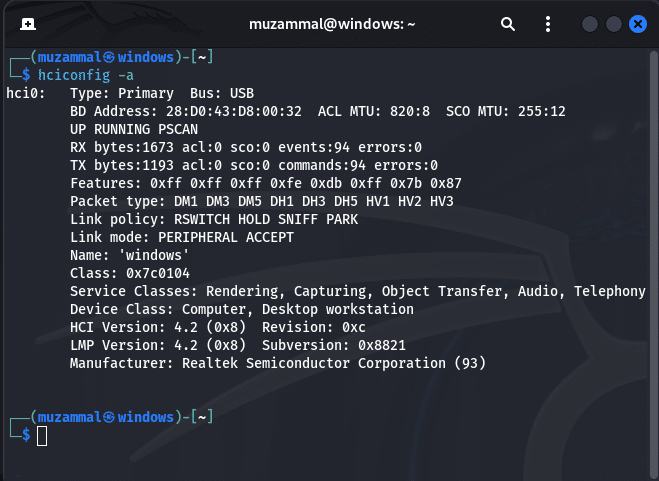
If you see “UP RUNNING” in the output, it’s live and kicking. You can also run:

bluetoothctl showThis command shows more information about your current Bluetooth setup, including whether it’s discoverable by other devices.
Pair and Connect Your Devices
At long last, it’s time to pair your Bluetooth item. Open the bluetoothctl tool and run the following:
Allow scanning via scan to discover nearby devices:
scan on
Find your devices mac address in the list (ex. 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC).
Pair with the device:
pair 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC
Connect to the device:
connect 00:11:22:AA:BB:CC
here is a small video about How to connect to your Bluetooth devices through terminal in Linux
If it works, you should hear a sound of confirmation (coming from your headphones) or get a notification on your device.
Common Troubleshoot:
Make sure the unit is pairing.
If you receive an error, disable Bluetooth and then re-enable it, and try again.
Even if you go through the process, you could still run into roadblocks. Here are some of these issues and what their solutions are:
Cannot Find Bluetooth Adapter:
Make sure you’ve plugged in the adapter and behave different USB slots. If you are on a VM, make sure usb passthrough is activated.
Bluetooth Service Not Starting:
To diagnose an error, use systemctl status bluetooth. Reinstall Bluez, if needed (sudo apt install --reinstall bluez).
Pairing Issues:
Make sure your device is in pairing mode. Try to pair and connect it manually via bluetoothctl.
No Bluetooth Icon:
Restart Kali Linux. I have even had the system UI not up date until a reboot.
Blocked Bluetooth:
Check for blocks with rfkill list and unblock with rfkill unblock bluetooth.
Wrapping Up
You don’t have to feel like you’re decoding an ancient script to get linux bluetooth not working. And with the right commands and a little patience, you will have flawless Bluetooth connection. Here’s a speedy list of the steps:
sudo apt bluetooth enable
- Enable Bluetooth service:
sudo systemctl enable bluetooth.service. - Start Bluetooth service:
sudo systemctl start bluetooth.service.
3.Start Bluetooth enable service: sudo systemctl start bluetooth.service
Still encountering issues? Feel free to look through the Linux forums, or ask in the comments for help! If you’re interested in learning more about why Linux is so great, or why the Linux operating system may be the place to start for faster, safer computing, you can do so in other articles that we posted here.